TEST SET Lock
Synchronization mechanism- uses test and set instructions to provide the synchronization among the processes executing concurrently.
Analysis of Test And Set Lock:
Mutual Exclusion:
Mutual Exclusion is guaranteed in TSL mechanism since a process can never be preempted just before setting the lock variable. Only one process can see the lock variable as 0 at a particular time and that's why, the mutual exclusion is guaranteed.
Progress:
According to the definition of the progress, a process which doesn't want to enter in the critical section should not stop other processes to get into it. In TSL mechanism, a process will execute the TSL instruction only when it wants to get into the critical section. The value of the lock will always be 0 if no process doesn't want to enter into the critical section hence the progress is always guaranteed in TSL.
Bounded Waiting:
Bounded Waiting is not guaranteed in TSL. Some process might not get a chance for so long. We cannot predict for a process that it will definitely get a chance to enter in critical section after a certain time.
Architectural Neutrality:
TSL doesn't provide Architectural Neutrality. It depends on the hardware platform. The TSL instruction is provided by the operating system. Some platforms might not provide that. Hence it is not Architectural natural.
Demo
Steps
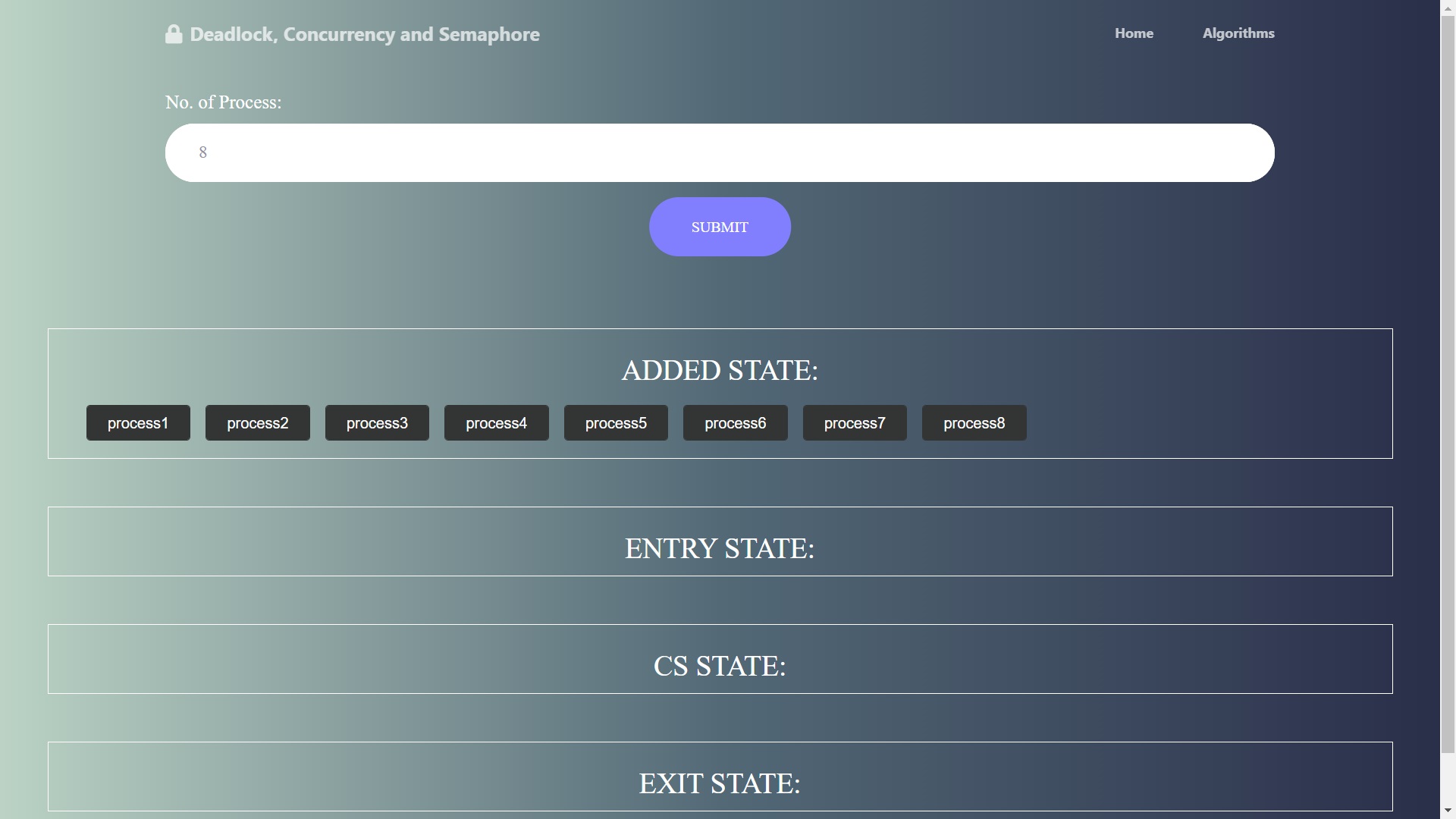
Input
Enter the number of process required and that will be shown in the added state.
For processing the process further click on the respective process and that will be added to the new state according to the algorithm or alert will be shown.
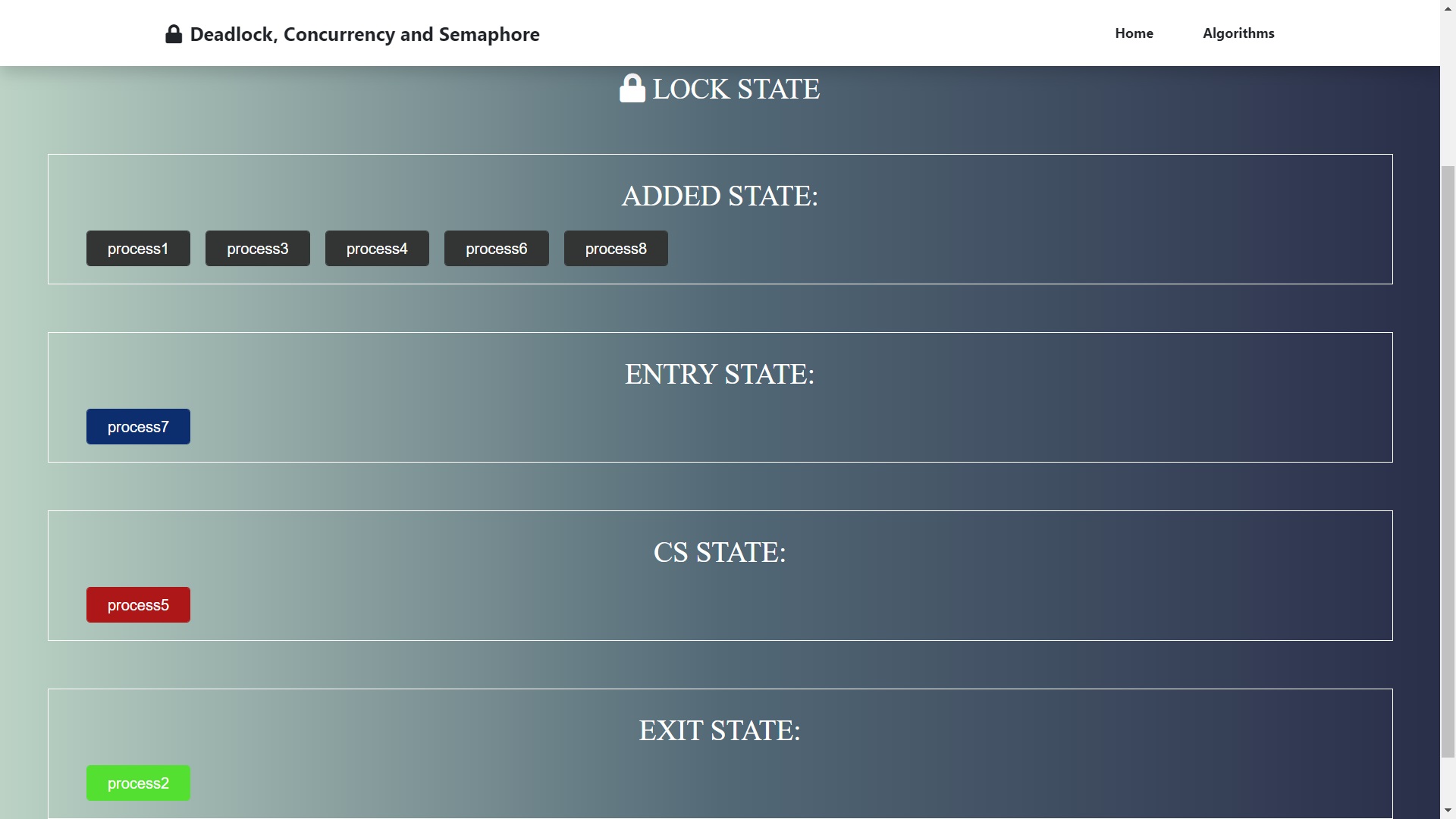
Output
The output will be according to the user input on the respective process for different states.
The lock state is shown above the added state according to the process in the critical state.